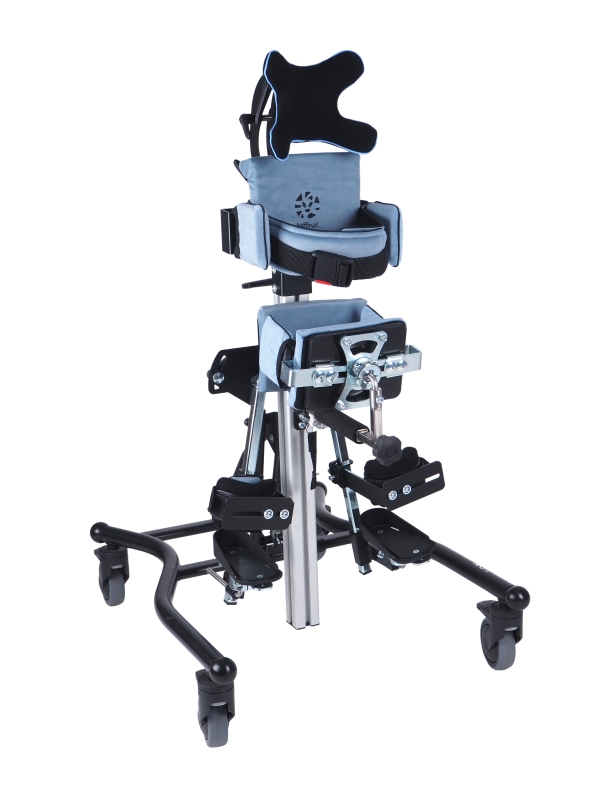
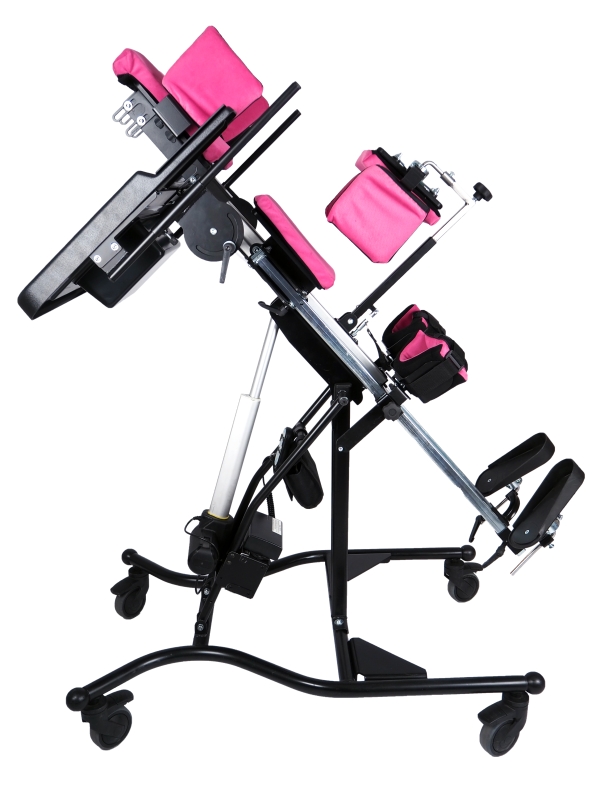
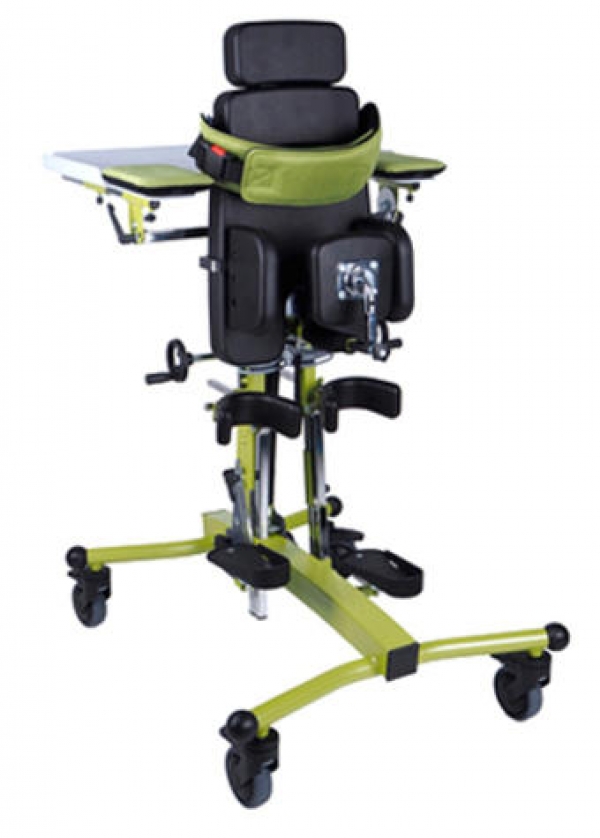
Positioning - maintaining a permanent and stable posture based on two lower limbs, enabling a person to better perceive the world. The ability to permanently maintain a vertical position has become a distinguishing feature of our species distinctiveness among other mammals. Depending on the motor skills of the patient in this group of orthopedic equipment, we can distinguish front standing stands for people with better head control and rear stands for people who have weaker control of the head position in relation to the rest of the body.
Why and for whom are the standing devices dedicated
In addition to the well-known beneficial effects of upright standing on the circulatory, respiratory and nervous systems, standing positively affects the reconstruction of the proximal part of the femur - reducing the cervical-molar angle and cervical anthorosis. In addition, it helps to maintain the correct length of the muscles: ischio-shin, internal hip rotators and adductors, which facilitates the correct setting of the pelvis. The lack of upright standing causes systemic changes, not local ones. Hence, upright standing is necessary for the organism, the human body, and its overall physical, mental and emotional comfort.
In the process of rehabilitation with the use of upright standing, it is very important to remove pathological patterns and to conduct it in such a way that the created new patterns are as close to the correct ones as possible. They are supposed to prevent the development of pathological motor skills, therefore the upright positioning can be started quickly even just after 10 months of age. is very important. Thanks to appropriate upright positioning, we preserve the effects of the therapists' hard work and prevent abnormal movement patterns from consolidating during breaks in improvement.
Depending on the patient's motor skills, we can divide them into front and back, and we can also categorize them as dynamic (they enable movement) and static, as well as into verticalizers with the hip abduction function.
Uprighting children with hip problems is essential for the proper development and avoiding pain of the patient. In recent years, many advantages of upright standing children have been studied, including With abduction, it was written that the early use of posture management equipment played a role in reducing hip problems. For this reason, standing programs are often part of an attitude management program and are recommended for children with neurological deficits who are not standing by the age of 12–18 months. Upright programs facilitate vertical alignment, increase lower limb load-bearing capacity, improve antigravity posture, increase strength and endurance, cope with contractures, prevent leg crossing, aid acetabular development, and prevent hip dysplasia. It is recommended that children with MPD, aged 10–12 months, be started on a daily loading program as part of a regular program.
An absolute contraindication to standing upright with abduction is habitual dislocation in the hip joint (when the hip joint "pops out" from the acetabulum).
Positioning - for whom?
The standing frames are most often used in the following diseases: cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophies, paralysis of various origins, spinal bifurcation, meningeal hernias, conditions after spinal injuries, conditions after craniocerebral injuries, conditions after stroke, postural defects, especially scoliosis spine or when other supplies are not applicable.

 Polski
Polski  English
English